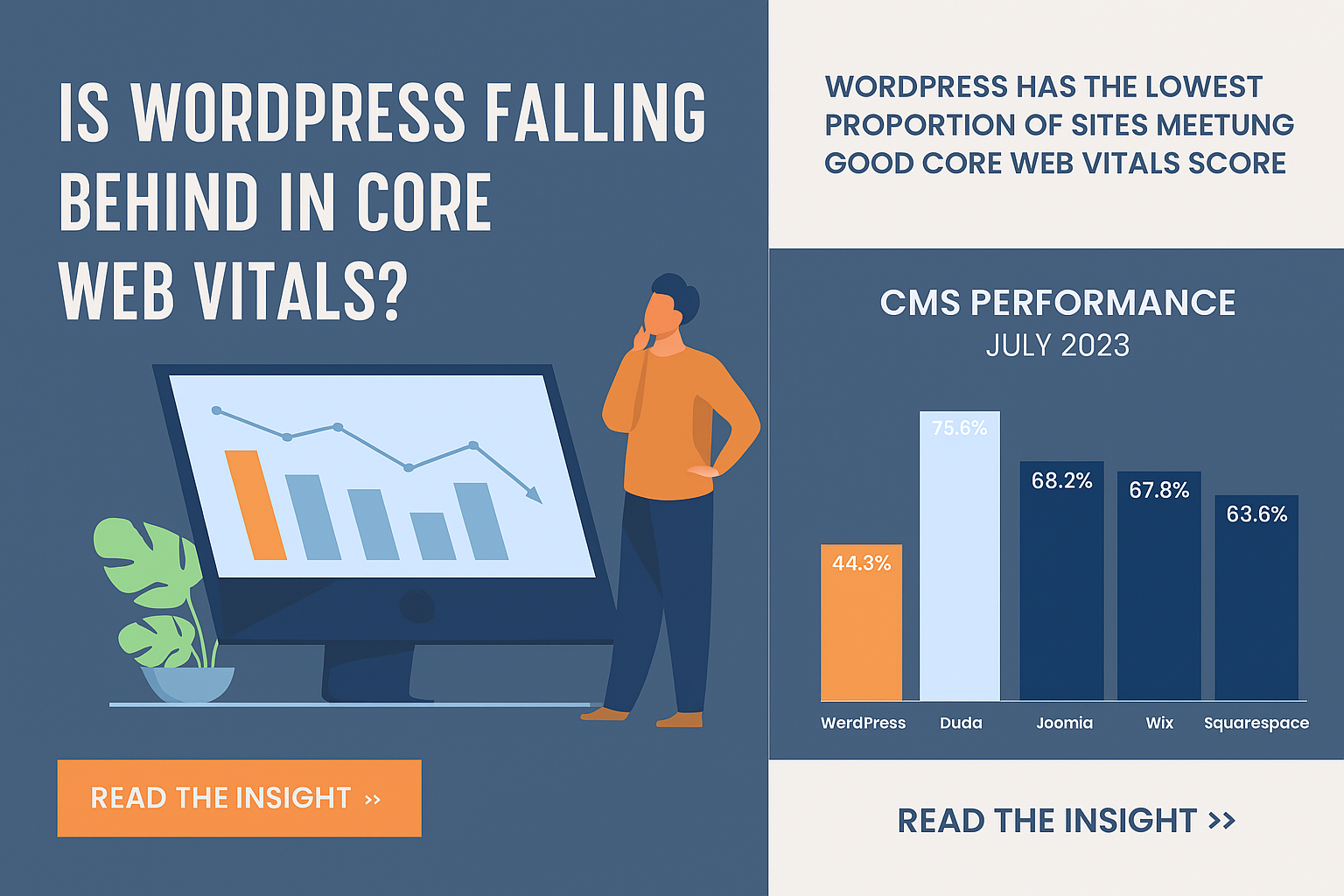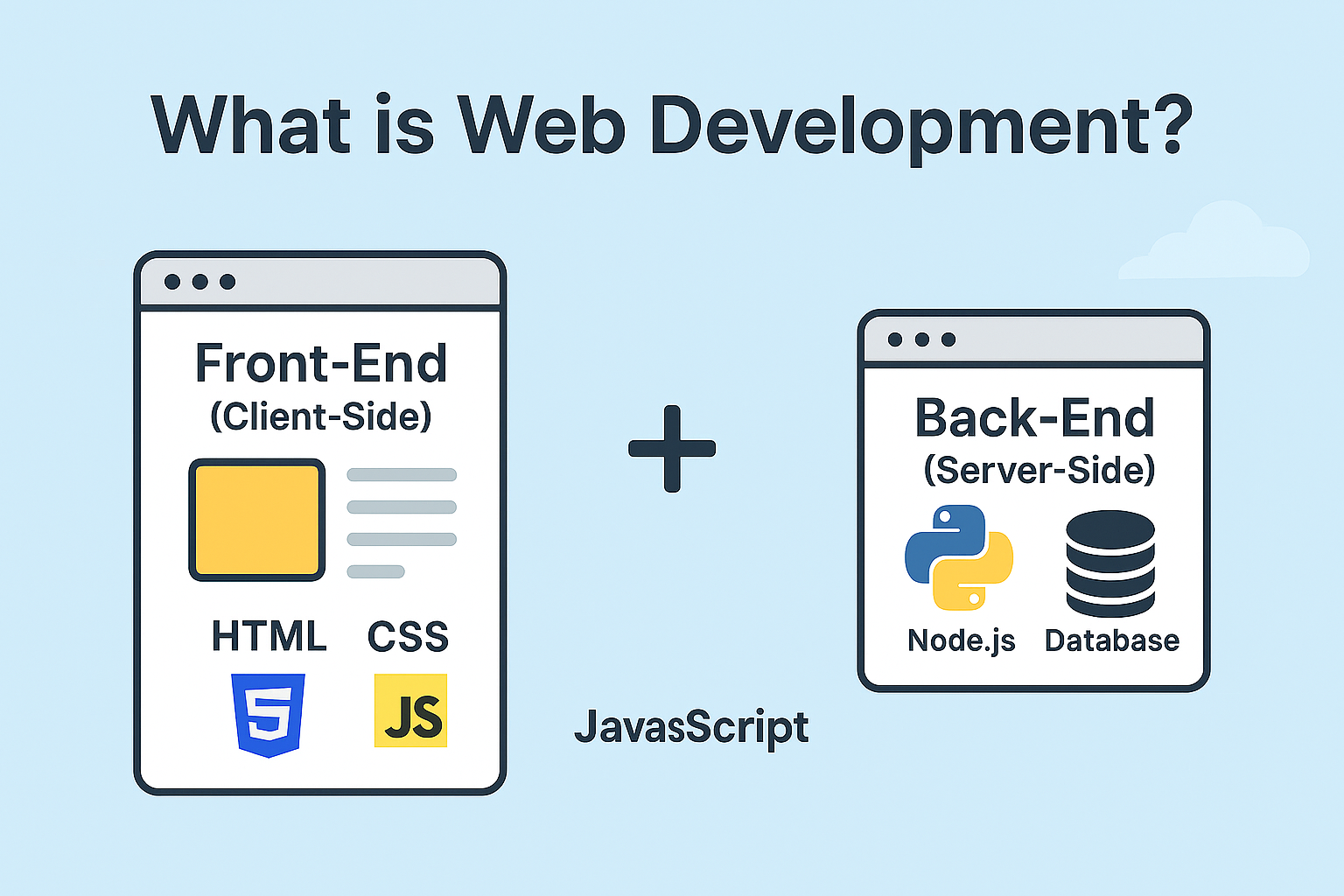
Web development might sound complex, but at its core, it’s just about building and maintaining websites. Whether you’re scrolling through an e-commerce store, watching a video, or reading a blog, every click and interaction is powered by web development.
Let’s break it down into simple parts so you can understand how websites come to life.
1. Front-End (Client-Side) – The Face of Your Website
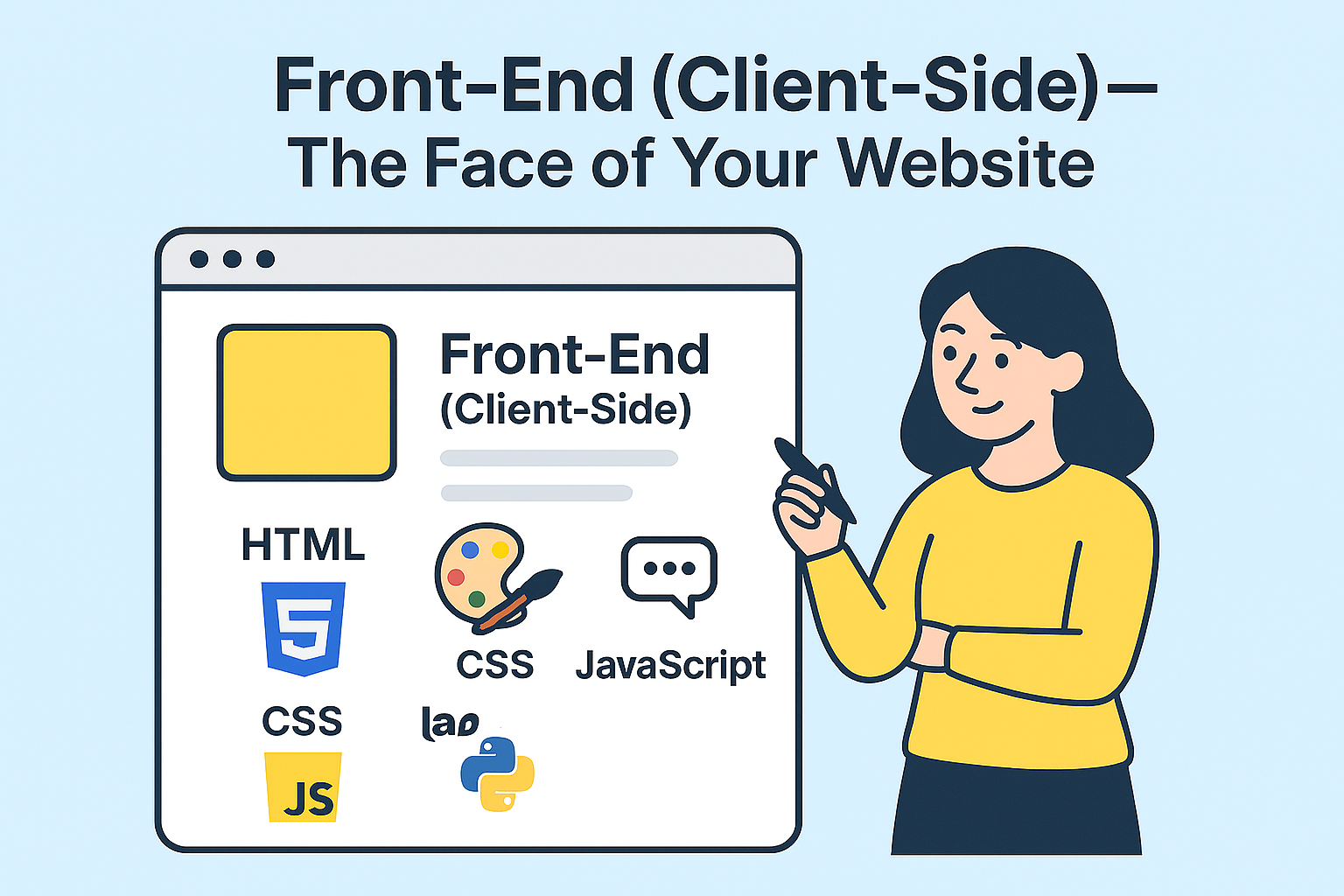
The front-end is everything you see on a website. From the layout and colors to the buttons you click, it’s all designed to create a smooth user experience.
Key Languages:
- HTML → Provides the structure of the website (like the foundation of a building).
- CSS → Adds design, colors, and styles (the paint, furniture, and décor).
- JavaScript → Makes things interactive (buttons, forms, animations, etc.).
Popular Frameworks:
- React, Vue, Angular → Help in building dynamic, scalable, and faster applications.
Useful Libraries:
- jQuery → Simplifies complex JavaScript tasks.
- Bootstrap, Tailwind CSS → Offer ready-to-use components and responsive designs.
In short, the front-end is the “face” of your website—what your visitors see and interact with.
2. Back-End (Server-Side) – The Engine of Your Website
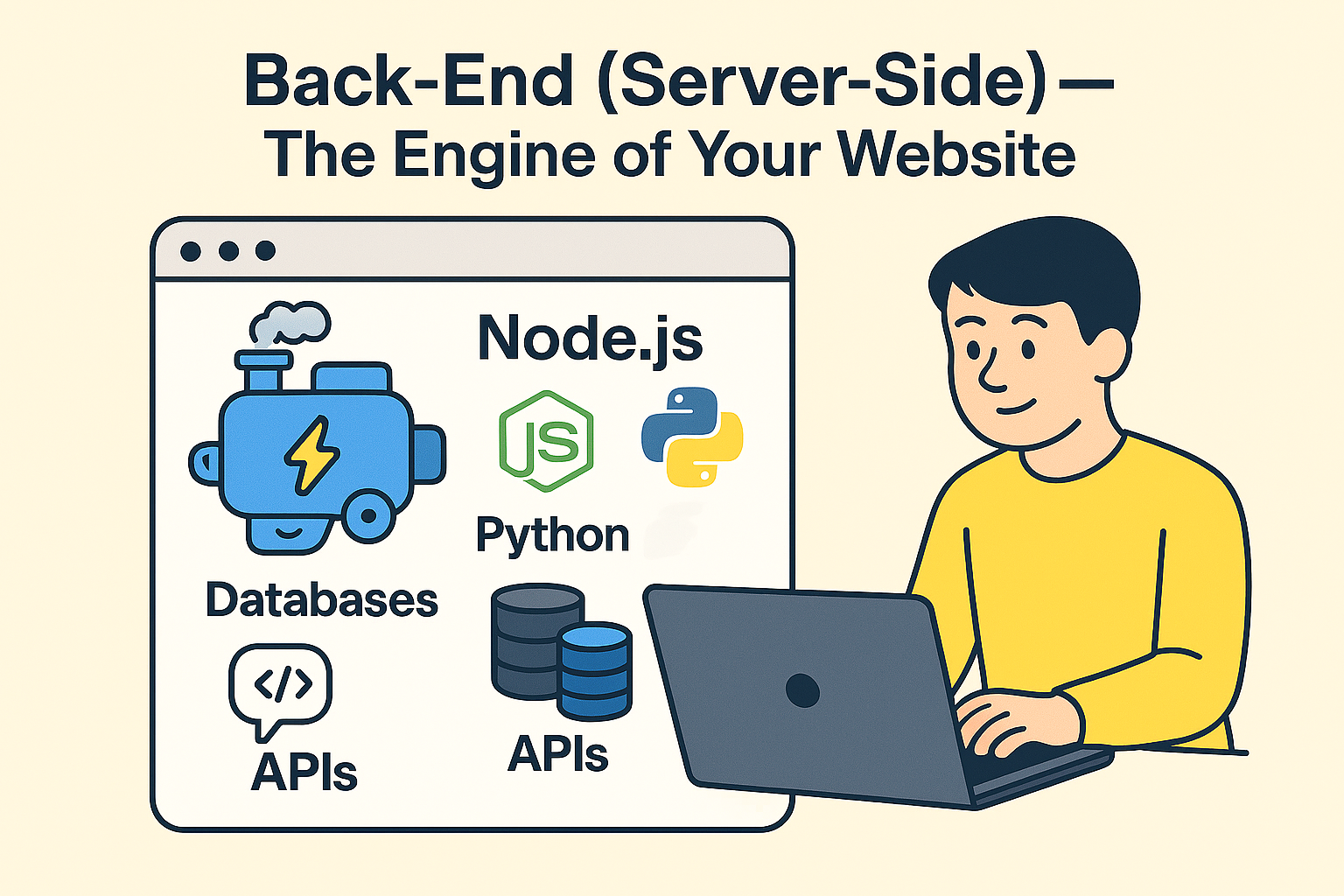
While the front-end focuses on what users see, the back-end is what happens behind the scenes. It’s like the engine of a car—you don’t see it, but it powers everything.
Key Languages:
- Node.js (JavaScript for servers)
- Python, PHP, Ruby, Java
Databases:
- MySQL, PostgreSQL → Store structured data (like user accounts or product listings).
- MongoDB → A NoSQL database that stores flexible data (great for apps with changing data).
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces):
- REST & GraphQL → Work as bridges that connect your front-end with your back-end.
The back-end ensures data is stored, retrieved, and processed correctly—making your website functional and reliable.
How It All Works Together
Think of a website as a team where every part has its role:
- Front-End = User Interface (design and interaction)
- Back-End = Logic + Database (processing, storing, and managing data)
- API = Bridge (communication between the two)
When combined, these create a complete, dynamic, and interactive web application.
Pro Tip for Beginners
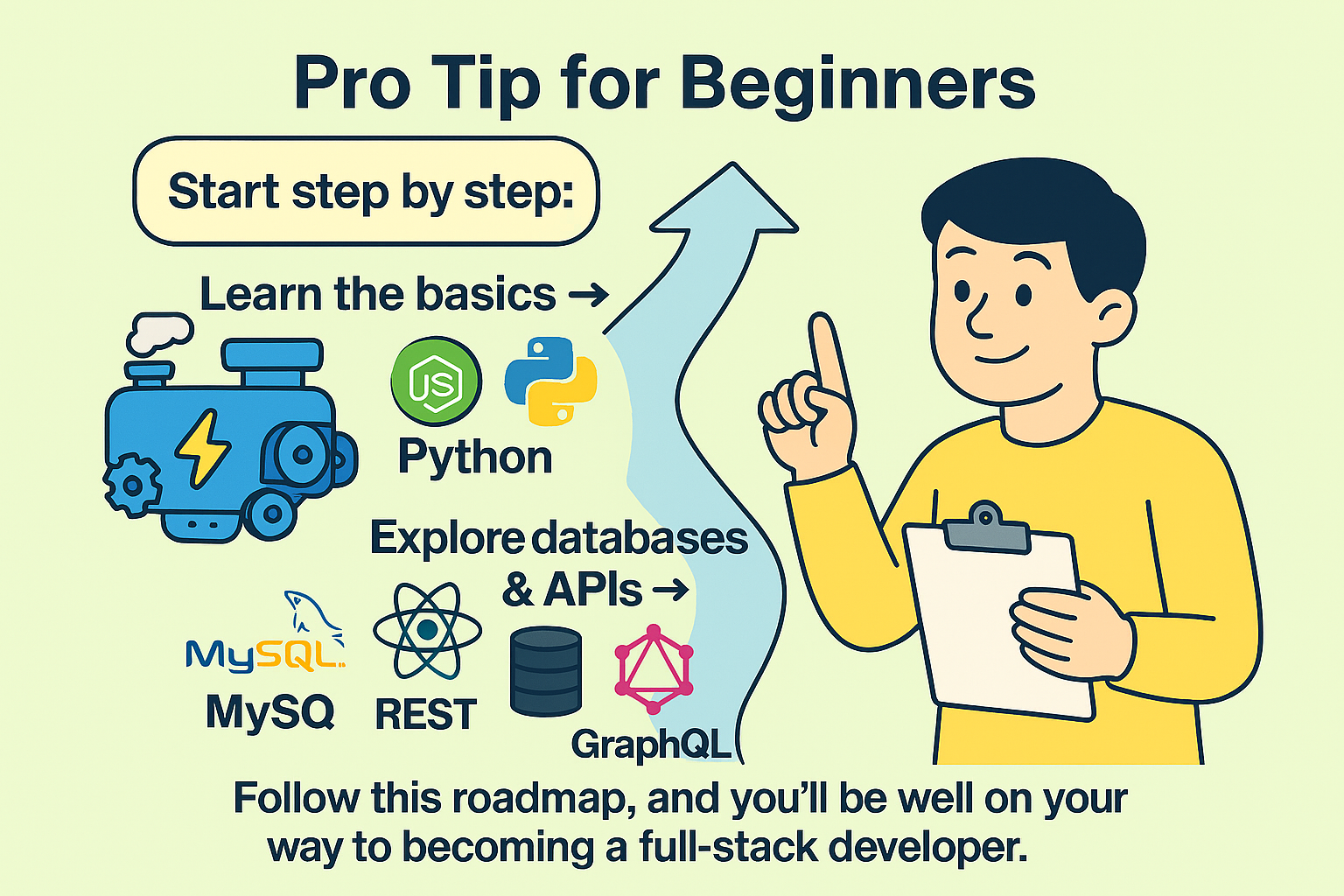
If you’re new to web development, don’t get overwhelmed. Start step by step:
- Learn the basics → HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Move on to frameworks → React (front-end), Node.js (back-end).
- Explore databases & APIs → MySQL, MongoDB, REST, GraphQL.
Follow this roadmap, and you’ll be well on your way to becoming a full-stack developer.
At BizzNist, we simplify IT knowledge for businesses and learners. Web development doesn’t have to be intimidating—once you understand the building blocks, the possibilities are endless.