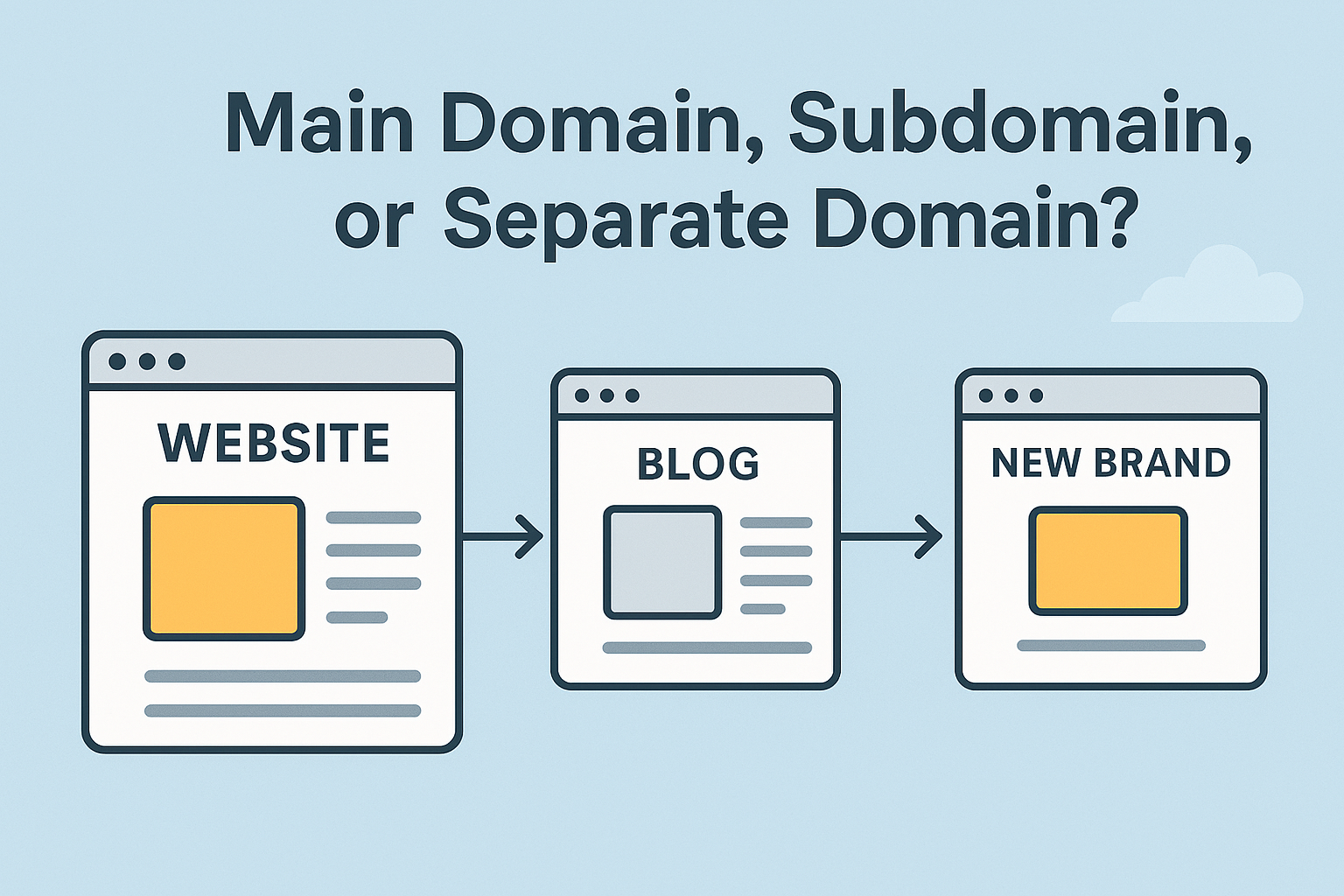
When a website expands, businesses often add new features—such as blogs, online stores, forums, learning platforms, or digital products. At this stage, an important question arises:
Should the new feature be hosted on the main domain, a subdomain (feature.example.com), or a completely separate domain (newbrand.com)?
This decision can affect branding, SEO, user experience, and long-term scalability. Let’s break down the options.
1. Hosting Everything on the Main Website (example.com/feature)
Advantages:
- Unified Brand Presence – All services remain under a single identity, boosting recognition.
- SEO Authority – New pages benefit from the domain’s existing SEO strength.
- Simplified Tracking – Analytics and conversions are easier to monitor in one place.
- Seamless User Experience – Visitors don’t feel like they are leaving the main site.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Site Management – Adding too many features can make the website heavy or confusing.
- Technical Limitations – Some tools or platforms may not integrate smoothly.
- Performance Risks – Resource-heavy features (e.g., video hosting, online shop) can slow down the main site.
2. Hosting Features on a Subdomain (feature.example.com)
Advantages:
- Clear Separation – Keeps services independent and easier to manage.
- Stable Performance – The main site stays lightweight while the subdomain handles heavy tasks.
- Brand Continuity – Still connected to the main brand name, building trust.
- Technical Flexibility – You can run a different CMS or platform on the subdomain without affecting the main site.
Disadvantages:
- SEO Challenges – Search engines often treat subdomains separately, so you’ll need fresh SEO efforts.
- Extra Setup – Requires separate SSL, hosting, and security management.
- User Confusion – Some visitors may feel redirected to a “different” site.
3. Hosting Features on a Separate Domain (newbrand.com)
Advantages:
- Independent Branding – Allows the new platform to grow into its own identity.
- Full Creative Control – Design and messaging can be completely different.
- Risk Isolation – Any downtime or issues on one domain won’t affect the other.
Disadvantages:
- No Shared Authority – SEO ranking must start from zero.
- Brand Disconnect – Users may not connect the new domain to your existing brand.
- Extra Marketing Effort – Requires dedicated promotion and backlinks.
4. Key Factors to Consider
Before choosing, evaluate:
- Your Long-Term Goals – Is this feature a small add-on or a standalone business idea?
- SEO Strategy – Do you want to leverage your existing SEO authority or build a fresh one?
- User Journey – Will moving to a subdomain or new domain create confusion?
- Technical Needs – Can your current CMS handle the feature efficiently?
5. Recommended Approach
For most businesses, a subdomain (e.g., shop.example.com, blog.example.com) is the balanced choice:
- Keeps the brand consistent
- Allows technical freedom
- Avoids slowing down the main website
If your new feature is planned to become a standalone brand, then a separate domain is a stronger long-term move.
Conclusion
Choosing between a main domain, subdomain, or separate domain is not just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. The right choice depends on your branding, SEO goals, technical setup, and long-term vision.
At BizzNist, we help businesses build and scale websites with the right domain structure, SEO strategy, and seamless user experience.